Introduction to Wildfire Events
Wildfire events represent a significant and complex interplay between natural phenomena, human activity, and climate conditions. These uncontrolled fires can lead to devastating ecological, economic, and social repercussions. As a burgeoning concern in our rapidly changing world, a deep understanding of wildfire events is crucial to foster awareness and develop effective preventive measures. This article delves into the anatomy of wildfire events, exploring their definitions, causes, consequences, and preventive strategies. For more detailed insights into wildfire events, we will also consider emerging trends and the future outlook on wildfire management.
Definition and Types of Wildfire Events
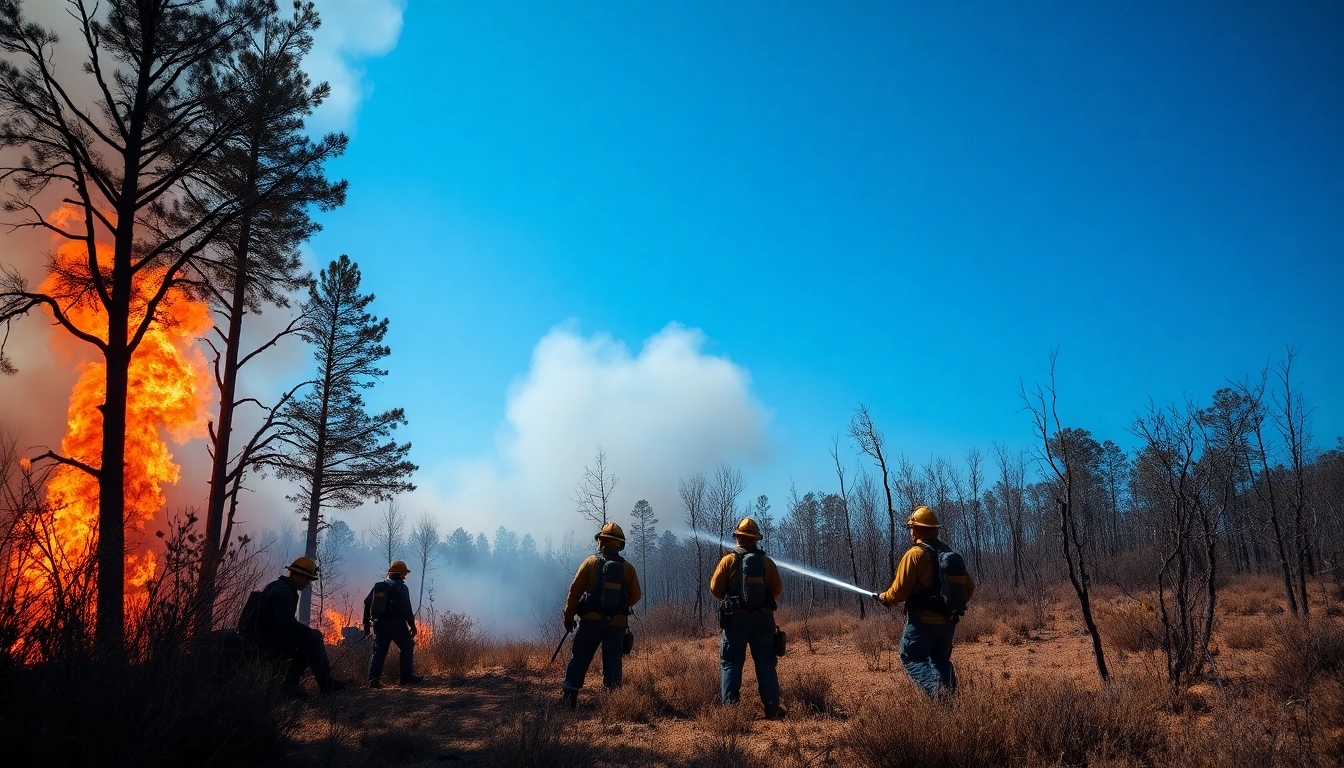
Wildfire events refer to large, uncontrolled fires that ignite in wildland areas, posing threats to both ecosystems and communities. They can be classified broadly into three types: surface fires, ground fires, and crown fires.
- Surface Fires: These fires burn vegetation on the surface layer including grasses, shrubs, and small trees. They move relatively slowly, typically aided by wind and moisture levels.
- Ground Fires: This type occurs below the surface litter and can smolder for extended periods, often fueled by organic matter in the soil.
- Crown Fires: Often the most devastating, crown fires spread rapidly through the treetops, usually in wind-driven situations, making them particularly challenging to control.
Importance of Wildfire Awareness
Understanding wildfire dynamics is critical for several reasons. Firstly, it equips communities with knowledge to mitigate risks and respond effectively to wildfire threats. Secondly, as climate change intensifies, awareness enables better planning for wildfire management and disaster response. Public education initiatives such as Fire Prevention Week and community workshops play pivotal roles in raising awareness, leading to stronger community resilience against wildfires.
Historical Context of Wildfire Events
The frequency and intensity of wildfire events have evolved over decades, particularly increased by anthropogenic factors. Significant historical wildfires, such as the Great Fire of 1910 in the United States, resulted in sweeping changes in fire management policies. Understanding these historical contexts provides insight into ongoing challenges, guiding modern wildfire prevention strategies.
Causes and Conditions for Wildfire Events
Natural Causes of Wildfire Events
Wildfires can ignite due to natural causes like lightning strikes and volcanic eruptions. Lightning serves as one of the primary ignitors in many regions, particularly during dry conditions that predispose vegetation to combustion. Soil and local environmental factors also contribute to the likelihood of wildfires in a given area.
Human Influence on Wildfire Incidents
Human activity exacerbates wildfire events considerably. Factors such as land-use changes, campfires left unattended, discarded cigarettes, and even arson substantially increase the frequency of wildfires. Urban development patterns often lead to the encroachment of human settlements into fire-prone areas, escalating the risks posed by wildfires. The implementation of community regulations and responsible land management practices can help minimize human-induced risks.
Climate Change Impact on Wildfires
Climate change significantly affects the incidence and intensity of wildfire events. Rising temperatures contribute to prolonged drought periods, leading to drier vegetation that ignites more easily. Additionally, climate change influences weather patterns, thereby enhancing conditions conducive to wildfires, such as increased winds and reduced humidity. Understanding these impacts is essential for developing adaptive management strategies aimed at lessening the severity of future wildfire scenarios.
Consequences of Wildfire Events
Environmental Effects of Wildfire Events
Wildfires generate extensive environmental concerns, from the immediate destruction of habitats to long-term soil degradation, water quality issues, and atmospheric pollution. While some ecosystems evolve with fire as a natural regenerative process, rampant wildfires can upset this balance, leading to biodiversity loss and ecosystem services disruption.
Economic Implications of Wildfire Incidents
The economic aftermath of wildfire events can be staggering. Direct firefighting costs, property damage, and loss of income due to business disruptions contribute to a long list of financial consequences. Furthermore, the indirect costs associated with health issues stemming from smoke inhalation and rehabilitation efforts further complicate the economic landscape.
Social and Community Consequences
Wildfires not only endanger lives but also displace communities and disrupt social structures. The psychological impact on affected populations can lead to long-term mental health challenges. Communities that emerge from wildfire experiences often grapple with trauma, loss, and the arduous journey of rebuilding and recovery.
Strategies for Wildfire Prevention
Community Preparedness for Wildfire Events
Community preparedness is paramount in mitigating the impacts of wildfire events. Local governments and organizations can establish fire-safe programs, offer educational workshops, and initiate neighborhood notification systems to raise awareness and improve readiness. Additionally, conducting regular hazard assessments helps identify susceptible areas and facilitate strategic planning.
Fire Management Techniques
Effective fire management techniques include controlled burns, forest thinning, and removal of hazardous fuels. Controlled burns help reduce fuel accumulation, thereby lessening the intensity of potential wildfires. Regular forest management and restoration efforts can restore ecosystems, making them more resistant to wildfire impacts.
Role of Technology in Preventing Wildfire Events
Innovative technologies, including satellite imaging and drone surveillance, are playing increasingly critical roles in wildfire prevention and management. Remote sensing technology offers real-time data to monitor wildfire risks and track active fires, enabling quicker responses. Predictive software models also assist in anticipating fire behavior, providing valuable information to emergency response teams.
Current Trends and Future Outlook on Wildfire Events
Emerging Patterns in Wildfire Incidents
Recent trends indicate an uptick in the frequency, severity, and geographic spread of wildfire events worldwide. Research highlights growing concern regarding larger fire seasons extending into traditionally stable periods. Tracking these patterns is vital for anticipating shifts in wildfire behavior and preemptive planning.
Legislation and Policy Changes
Legislative initiatives aimed at enhancing wildfire management frameworks are critical for reducing risks. For instance, policies increasingly focus on land-use planning, funding for wildfire research, and support for community-based initiatives that promote resilience against wildfires. Continued advancements in public policy will play a key role in diminishing the impacts of future wildfire events.
Innovative Solutions for Wildfire Management
The future of wildfire management looks promising with continuous developments in technology and community strategies. Innovations such as artificial intelligence in predictive analytics for fire behavior and partnerships between governmental agencies and the private sector are becoming crucial for cohesive wildfire strategies. Emphasizing collaborative approaches that combine community engagement with cutting-edge technology will likely shape the future of effective wildfire management.